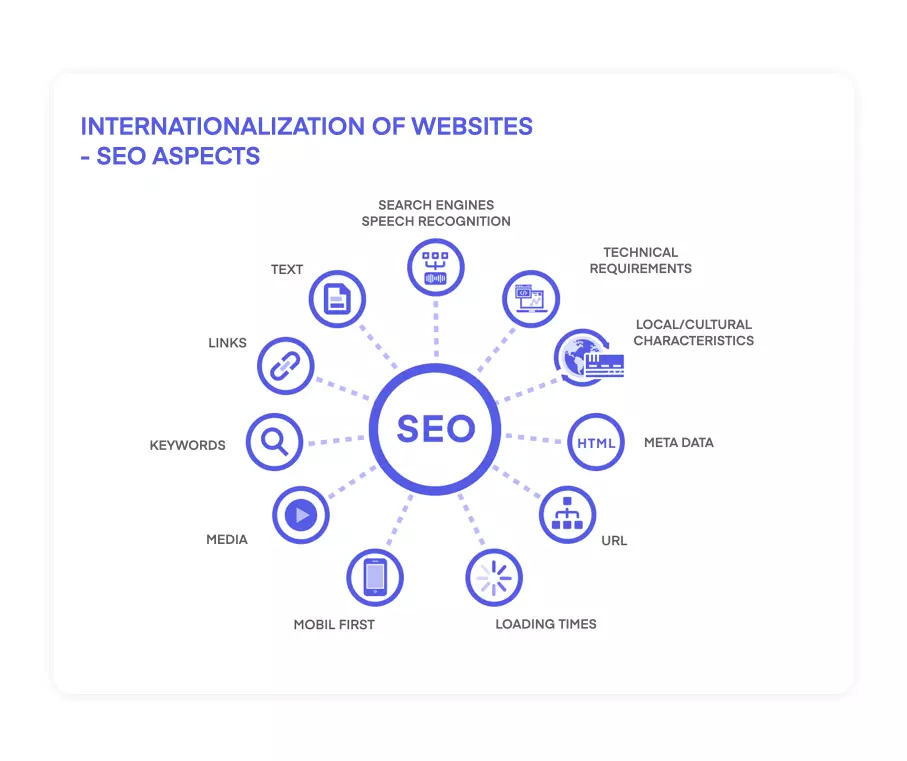
SEO-RELEVANT INTERNATIONALIZATION
Especially when internationalizing website content from an SEO perspective, there are several factors to consider in order to achieve a good ranking for the different language variants of the website on the one hand, and to avoid mutual competition between the individual pages on the other.
711media as your SEO agency
Technical requirements for SEO-relevant texts
However, before we start designing the texts for other country pages, we must first ensure that the technical requirements are met:
Characters from different fonts can be offered and thus displayed in the same system
Different writing directions must be taken into account (left-right, right-left, top-bottom, etc.)
Some languages have several writing variants (e.g. Serbian with Cyrillic script or Latin script)
For example, capitalization does not exist in every font
Although the Gregorian calendar is usually used as the basis for the calendar system in other languages, it sometimes makes sense to use regional formats and time calculations
A distinction is made, for example, between 24-hour and 12-hour counting, which are indicated with a.m. and p.m. respectively for clear identification
Currencies, weights, measurements, decimal and thousands separators, etc.
On the one hand, software must be able to take different times into account, and on the other hand, it must be able to display the time to every website visitor in the appropriate format and converted to the corresponding time zone
Observe local / cultural Particularities
In international (business) relationships, it goes without saying that you should consider the culture of your counterpart in advance and implement or avoid certain customs: Do you shake hands in greeting or is it better to bow? How do you dress for which occasion? Where are business meetings held, in the office or in a restaurant, and who pays the bill afterwards?
It is therefore obvious that cultural peculiarities not only arise in personal contact with other cultures, but also in the internationalization of websites.
Some cultural aspects, such as country-specific writing styles, have already been discussed in this article. However, there are many more cultural peculiarities to consider, as national standards dominate international (size) systems:
Navigation elements
In conjunction with the correct writing direction, the reading direction also goes hand in hand and therefore also where the navigation elements are to be found on the website. For example, in German, a drop-down menu is usually found at the top right. In Arabic, this should be at the top left of the respective pages.
Names and titles
The correct form of address, first name, surname and title are also culturally different. For example, forms on websites must be adapted accordingly in order to be able to display longer names in full. The use of "diverse" or "no selection" in salutations should also be implemented.
State-assigned numbers
For example, VAT identification numbers, ID card numbers or social security numbers are written differently in each country. Some contain fewer, some more numbers, sometimes even letters. These factors must be taken into account.
Number formats, units, addresses and telephone numbers
Adjustments must be made for the internationalization of a website, especially for contact forms. This is because not every country has a zip code as is usual in Germany, but provinces or regions must be specified.
Local payment providers
As with all other points, there are of course often other payment providers that are preferred in other countries. These should also be offered in order to radiate a certain seriousness and trustworthiness. Examples:
- China: Alipay, Tenpay, UnionPay
- Netherlands: iDEAL
- Poland: Przelewy24
Paper dimensions
Although many countries now use standardized paper dimensions according to the DIN standard, not all of them do. Japan and North America, for example, have different formats, which must be taken into account. Particularly in the case of print media or media that are suitable for downloading and may be printed out.
Text content
Once all technically relevant conditions have been defined, analyzed and implemented, the actual page content is created. This content in particular should be optimized for search engines, as it has a decisive influence on the subsequent ranking.
A distinction must first be made between Google and other search engines. In China, the primary search engine is Baidu, in Russia it is Yandex, for which other ranking factors play a role, which is partly due to different characters or spellings.
Due to different writing and reading styles, it is particularly advisable for Arabic countries to design their own layouts for the website and use templates optimized for the respective language.
Text content
If 1:1 translations are involved, translation tools should be avoided and native speakers should be consulted to guarantee correct formulations and sentence positions. In this case, however, hreflang and canonical tags must be used to avoid duplicate content.
However, specific translations for the respective languages would be better in order to achieve not only an internationalization but also a localization of the websites. As already mentioned, the focus keyword as well as the entire keyword set must be researched, analyzed and redefined accordingly, resulting in completely new text content. This is time-consuming, but recommended for a precise customer approach in the respective target markets.
Visual language
For example, for videos, icons, images, characters or colors. Just like navigation elements, images and videos are also subject to cultural characteristics. If possible, media should be used without integrated texts so that these can be inserted and adapted individually for each language.
In addition, great attention must be paid to the visual language. Unfortunately, depending on the culture, it is still a problem today when women are depicted. In addition, what causes a stir in Germany, for example, is considered offensive in many other cultures.
Colors are another stumbling block, because what is considered positive in one culture can have the exact opposite effect in another. For example, the color black is generally associated with death and mourning in Germany, while in Asian countries it is white and in South America it is orange.
As with colors, the same applies to icons, favicons and other symbols. In many countries, the upturned thumb means "one", "great" or "excellent". In Australia and Nigeria, on the other hand, it is understood to be a very vulgar insult. For this reason, great caution is also required with supposedly small things such as icons.
The flag navigation with pure flags as a recognition feature of the selected language can also pose challenges. For example, Ukrainians are just as difficult to find in the symbol of the Russian flag as Brazilians in the Portuguese flag. A combination of flags and international country codes should therefore be used here.
Special pages
Another special feature are pages such as terms and conditions, data protection, imprint, shopping cart and so on. This is because not every country requires and therefore has an imprint, shopping baskets can be structured differently and terms and conditions must contain different components. Caution is advised here!
Meta data
Not only the actual page content must be internationalized, the meta data must also be adapted and optimized for the respective language variants. This includes
- URL
- Page title
- Meta description
- Focus keyword and keyword set
- markups
- Images
- File URL
- Image title
- Image description
- Caption
- Alt text
- u. Social media tags, even if these are not SEO-relevant
All posts in the blog series "Internationalization" can be found here: